Unreal Scene Generation¶
SpaRRTa leverages Unreal Engine 5 to generate photorealistic synthetic images with precise control over object placement, camera positions, and environmental conditions. This enables the creation of a rigorous benchmark with mathematically precise ground-truth labels.
Why Synthetic Data?¶
Evaluation Environments¶
SpaRRTa includes five diverse high-fidelity environments to ensure robust evaluation across different visual domains:
Environment Details¶
Electric Dreams Environment
A sparse forest landscape with complex foliage, uneven terrain, and natural rock formations. This environment tests spatial reasoning in organic, unstructured settings.
- Source: Electric Dreams (Epic Games)
- Characteristics: Complex foliage, uneven terrain, natural lighting
- Objects: Bear, Fox, Tent, Rocks, Trees
Arid Landscape
A vast, arid landscape characterized by open terrain, sand dunes, and high-contrast lighting. This environment is sparse and texture-homogeneous.
- Source: Realistic Desert Pack
- Characteristics: Open terrain, high contrast lighting, minimal occlusion
- Objects: Camel, Barrel, Cactus, Rocks
Eastern European Village
A snow-covered setting reflecting a typical small Eastern European town with cold lighting, snow textures, and village buildings.
- Source: Russian Winter Town
- Characteristics: Cold lighting, snow textures, village architecture
- Objects: Husky, Deer, Snowman
Valley Infrastructure
A valley scene centered around a large bridge infrastructure with mixed natural and man-made elements.
- Source: Automotive Bridge Scene
- Characteristics: Infrastructure elements, valley terrain, mixed complexity
- Objects: Bicycle, Trash Can, Vehicle
Modern Metropolis
A large-scale, modern American metropolis featuring high-rise architecture, paved roads, and complex urban geometry.
- Source: City Sample (Epic Games)
- Characteristics: Dense urban geometry, complex occlusion, varied lighting
- Objects: Motorcycle, Traffic Cone, Fire Hydrant
Asset Library¶
Asset Selection Criteria¶
Our asset selection follows specific criteria to ensure valid spatial reasoning evaluation:
- ImageNet Alignment: Objects align with common ImageNet super-categories to ensure VFMs can recognize them
- Isotropic Sources: Source objects (rocks, trees, cones) are rotationally symmetric to minimize orientation ambiguity
- Environmental Coherence: Objects naturally fit their respective environments (e.g., camels in desert)
- Visual Distinctiveness: Objects are clearly distinguishable from backgrounds and each other
| Category | Assets |
|---|---|
| Animals | Bear, Fox, Camel, Husky, Deer |
| Vehicles | Car, Taxi, Motorcycle, Bicycle |
| Nature | Trees, Rocks, Cactus |
| Objects | Tent, Barrel, Trash Can, Traffic Cone, Fire Hydrant, Snowman |
| Humans | Human agent (viewpoint for allocentric tasks) |
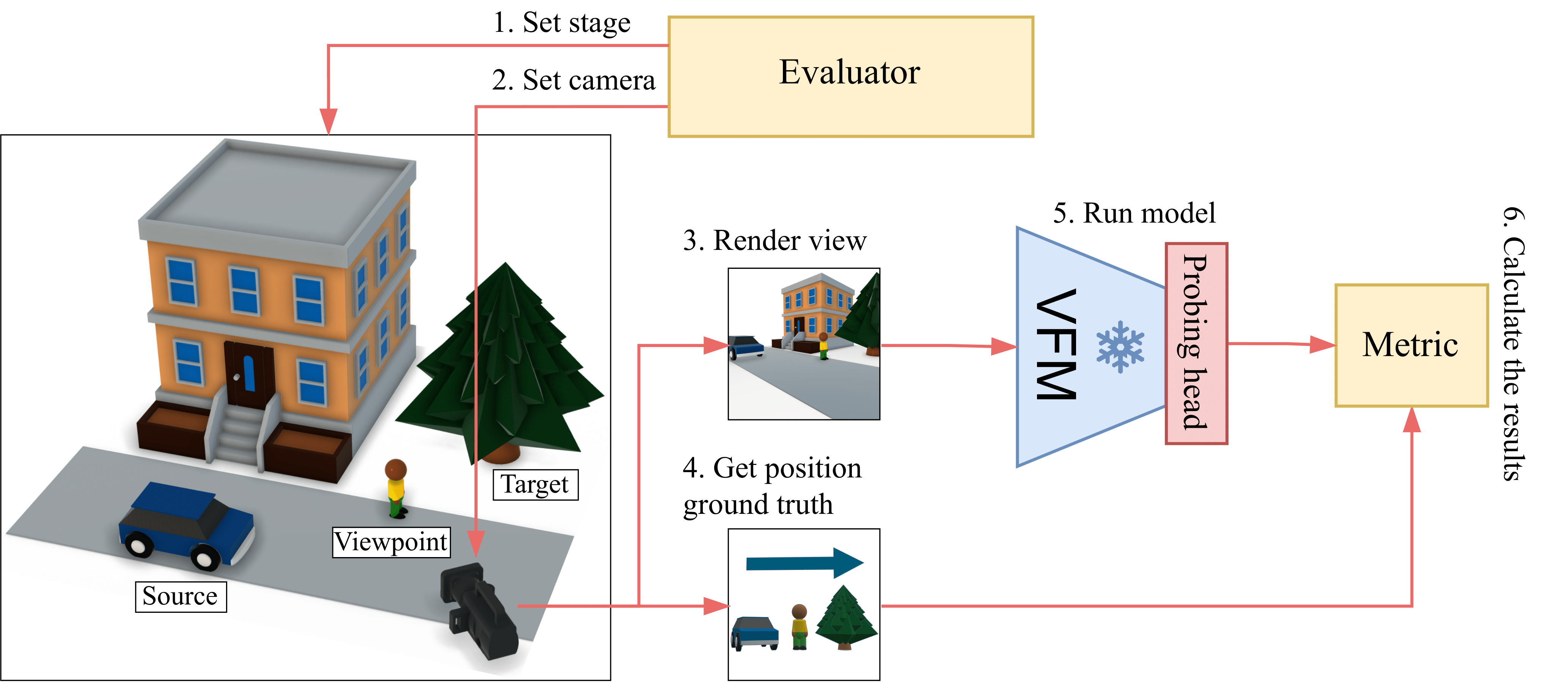
Data Generation Pipeline¶
Pipeline Steps¶
flowchart LR
A[Set Stage] --> B[Set Camera]
B --> C[Render View]
C --> D[Get Ground Truth]
D --> E[Run Model]
E --> F[Calculate Results]
style A fill:#7c4dff,color:#fff
style B fill:#7c4dff,color:#fff
style C fill:#536dfe,color:#fff
style D fill:#536dfe,color:#fff
style E fill:#3f1dcb,color:#fff
style F fill:#3f1dcb,color:#fff1. Set Stage¶
The evaluator establishes the scene configuration:
- Select environment (Forest, Desert, Winter Town, Bridge, City)
- Choose source, target, and viewpoint objects from the asset library
- Randomly sample object positions from a Gaussian distribution
- Apply physics-aware terrain adaptation via raycasting
2. Set Camera¶
Configure the viewpoint for image capture:
- Sample camera position within a defined area surrounding scene center
- Orient camera toward placed objects
- Validate visibility constraints (objects within field of view)
- Ensure proper scene composition (no extreme clustering or distance)
3. Render View¶
Generate high-fidelity imagery using Unreal Engine 5:
- Ray-traced RGB image with dynamic global illumination
- Ground-truth segmentation masks for validation
- Resolution: 2048x2048 - Later, it is downsampled to 224×224 (standard VFM input size)
4. Get Ground Truth¶
Extract spatial relation labels:
- Calculate angular relationship between source and target objects
- Apply viewpoint transformation (camera for ego, human for allo)
- Filter ambiguous configurations (objects near decision boundaries)
- Assign discrete label: Front, Back, Left, or Right
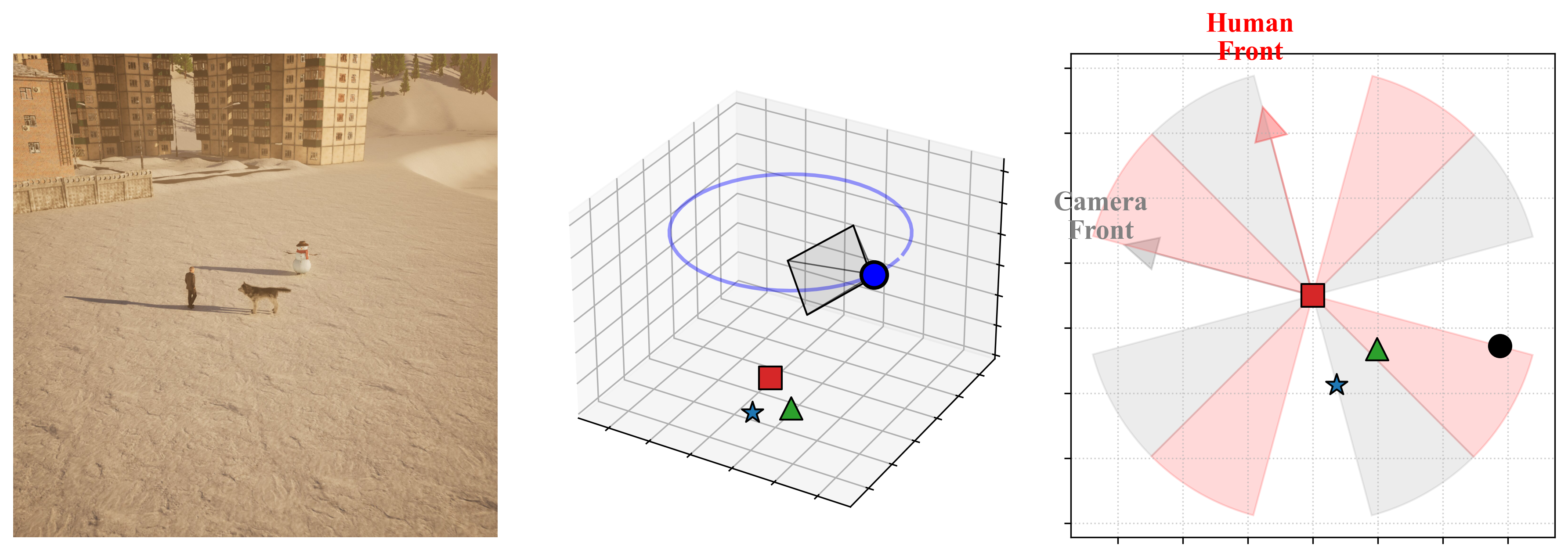
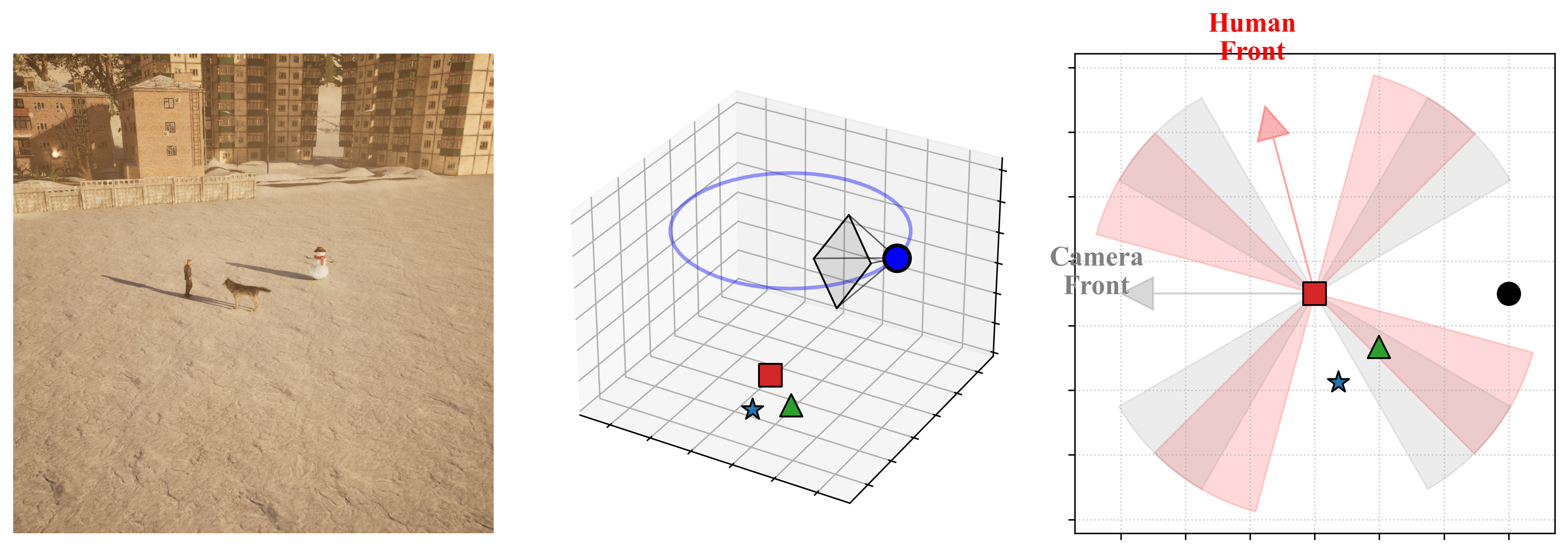
Geometric Ambiguity Control¶
A key challenge in spatial classification is defining precise boundaries between classes. SpaRRTa implements strict rejection sampling to eliminate label noise:
Exclusion Zones¶
Ambiguity zones are defined as conical regions centered along the diagonals:
- 45°, 135°, 225°, 315° relative to the viewpoint's forward vector
- Any sample where the target falls within these zones is automatically rejected
- This guarantees unambiguous ground-truth labels
Rejection Sampling
The pipeline automatically discards configurations where the target object lies within ±15° of a diagonal boundary, ensuring all retained samples have mathematically precise labels.
Technical Implementation¶
Rendering Stack¶
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine | Unreal Engine 5.5 |
| Lighting | Lumen (dynamic global illumination) |
| Geometry | Nanite (virtualized geometry) |
| API | Python Editor API + UnrealCV |
| Hardware | 2× NVIDIA RTX 2080 Ti (11GB VRAM) |
Camera Configuration¶
The camera system uses Unreal Engine's CineCameraActor with standardized settings:
def create_camera():
"""
Initialize CineCameraActor with standardized parameters.
"""
# Filmback settings (sensor dimensions)
sensor_width = 50.0 # mm
sensor_height = 50.0 # mm
# Lens settings
focal_length = 50.0 # mm
aperture = 10.0 # f-stop
# Calculate FOV from sensor and focal length
horizontal_fov = 2 * arctan(0.5 * sensor_width / focal_length)
vertical_fov = 2 * arctan(0.5 * sensor_height / focal_length)
# Result: ~53° horizontal FOV
fov = (horizontal_fov, vertical_fov)
# Create camera with these settings
camera = CineCameraActor(location, rotation)
camera.set_filmback(sensor_width, sensor_height)
camera.set_focal_length(focal_length)
camera.set_aperture(aperture)
return camera
Object Placement Algorithm¶
Objects are placed using an iterative rejection sampling approach with physics-aware terrain adaptation:
def place_objects(environment, objects, max_attempts=10):
"""
Place objects with physics-aware terrain adaptation.
Uses iterative rejection sampling to ensure valid configurations.
"""
# Sample center point for object cluster
center_x = sample_gaussian(environment_center_x, sample_radius)
center_y = sample_gaussian(environment_center_y, sample_radius)
center_z = environment_base_z
for attempt in range(max_attempts):
valid_placement = True
for obj in objects:
# Sample random rotation
rotation = random_rotation(yaw_range=(0, 360))
# Sample X, Y positions around center using Gaussian distribution
obj_x = random_gaussian(center_x, object_proximity_std)
obj_y = random_gaussian(center_y, object_proximity_std)
# Perform line trace to find ground height at (X, Y)
ground_z = detect_ground_at_position(obj_x, obj_y, center_z)
# Calculate proper Z position accounting for object bounds
# Get how much object extends below its origin
object_ground_offset = obj.get_ground_offset()
# Place object so bottom surface touches ground
spawn_z = ground_z - object_ground_offset + safety_margin
position = Vector(obj_x, obj_y, spawn_z)
obj.move_to(position, rotation)
# Validate configuration
for i in range(len(objects)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(objects)):
# Check for AABB overlap (collision detection)
if objects[i].overlaps(objects[j]):
valid_placement = False
break
# Check objects are not too far apart
if objects[i].distance_to(objects[j]) > max_distance:
valid_placement = False
break
if not valid_placement:
break
if valid_placement:
return True, (center_x, center_y)
# All attempts failed
return False, (center_x, center_y)
Camera Sampling with Screenshot¶
Camera positioning uses iterative sampling to ensure all objects are properly framed:
def sample_camera(camera, objects, object_center, max_attempts=15):
"""
Sample camera position and orientation with validation.
Ensures all objects are visible and properly framed.
"""
center_x, center_y = object_center
# Calculate average Z position of all objects
avg_object_z = mean([obj.get_location().z for obj in objects])
for attempt in range(max_attempts):
# Sample camera position around object cluster
camera_x = random_uniform(center_x - camera_range, center_x + camera_range)
camera_y = random_uniform(center_y - camera_range, center_y + camera_range)
camera_z = random_uniform(avg_object_z, avg_object_z + camera_height_range)
camera_position = Vector(camera_x, camera_y, camera_z)
camera.move_to(camera_position)
# Orient camera to look at centroid of all objects
object_centroid = calculate_centroid([obj.get_location() for obj in objects])
camera.look_at_many(objects)
# Validate all objects are within camera FOV
object_angles = []
for obj in objects:
# Calculate angle between camera forward vector and object
angle = camera.angle_to(obj)
object_angles.append(angle)
max_angle = max(object_angles)
min_angle = min(object_angles)
# Check objects are within FOV bounds
# Reject if any object is too far from center (outside FOV)
if max_angle > (camera.fov - margin):
continue # Reject and resample
# Reject if all objects are too close to center (too clustered)
if max_angle < min_angle_threshold:
continue # Reject and resample
# Valid camera configuration found
return True
# All attempts failed
return False
Iterative Rejection Sampling
The pipeline uses iterative rejection sampling with configurable maximum attempts:
- Object placement: Up to X attempts to find valid non-overlapping configurations
- Camera sampling: Up to Y attempts to find valid camera positions with all objects in frame
- Failed attempts are automatically discarded and resampled
Parameter Serialization
For each successfully generated scene, the pipeline serializes:
- Camera intrinsics (sensor dimensions, focal length, FOV, aperture)
- Camera extrinsics (position, rotation)
- Object positions and rotations
- All metadata saved to JSON files for reproducibility
Dataset Statistics¶
| Environment | Ego Images | Allo Images |
|---|---|---|
| Forest | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| Desert | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| Winter Town | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| Bridge | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| City | 5,000 | 10,000 |
| Total | 25,000 | 50,000 |
Dataset Size Rationale
- Egocentric: 5,000 images sufficient for generalization
- Allocentric: 10,000 images needed due to increased task complexity (perspective transformation learning)
Scene Visualizations¶
Explore interactive visualizations of generated scenes showing photorealistic renderings alongside their 3D spatial annotations and 2D top-down views.
Environment-Asset Relations¶
Each environment contains 3 unique object triples used for evaluation. The table below shows the complete mapping of environments to their source objects, target objects, and viewpoint configurations:
| Triple ID | Source Object | Target Object | Viewpoint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge-1 | Truck | Tree | Camera / Human 1 |
| Bridge-2 | Bike | Trash Bin | Camera / Human 2 |
| Bridge-3 | Vespa | Trash Bin | Camera / Human 3 |
| City-1 | Vespa | Cone | Camera / Human 1 |
| City-2 | Taxi | Fire Hydrant | Camera / Human 2 |
| City-3 | Bike | Cone | Camera / Human 3 |
| Desert-1 | Truck | Rock | Camera / Human 1 |
| Desert-2 | Camel | Cactus | Camera / Human 2 |
| Desert-3 | Camel | Barrel | Camera / Human 3 |
| Forest-1 | Tree | Rock | Camera / Human 1 |
| Forest-2 | Bear | Tent | Camera / Human 2 |
| Forest-3 | Fox | Rock | Camera / Human 3 |
| Winter-1 | Truck | Tree | Camera / Human 1 |
| Winter-2 | Husky | Snowman | Camera / Human 2 |
| Winter-3 | Deer | Tree | Camera / Human 3 |
Viewpoint Configuration
- Camera: Used for egocentric (SpaRRTa-ego) task evaluation
- Human 1 / 2 / 3: Different human models used for allocentric (SpaRRTa-allo) task evaluation, each with unique poses and positions